What is Market Capitalization?
Market capitalization (market cap) represents the total value of a company’s outstanding shares. It is calculated using the formula:
Market Cap = Share Price × Total Outstanding Shares
This metric helps investors gauge a company’s size, risk level, and potential for growth. Companies are generally classified into Small-Cap, Mid-Cap, and Large-Cap categories based on their market value.
Small-Cap Stocks (₹ 5,000 Cr or Below)
Small-cap stocks belong to companies with a market capitalization of ₹5,000 crore or lower. These stocks are known for their high growth potential but come with higher volatility and risk.
✔️ Key Features of Small-Cap Stocks:
✅ High Growth Potential: Small-cap companies can expand rapidly.
✅ Lower Institutional Interest: Mutual funds and institutional investors often avoid these stocks, leading to undervaluation opportunities.
✅ Higher Volatility: Price fluctuations are common due to lower trading volume and market speculation.
⚠️ Risks Involved:
❌ Liquidity Issues: Low trading volume may make buying or selling difficult.
❌ Market Sensitivity: Economic downturns can significantly impact these stocks.
🔹 Example Small-Cap Stocks:
- BSE: ₹4,500 Cr
- Zomato (Initial Phase): ₹3,200 Cr
Large-Cap Stocks (₹50,000 Cr & Above)
Large-cap stocks belong to well-established companies with a market cap of ₹50,000 crore or more. These companies are industry leaders and provide stable returns with lower risk.
✔️ Key Features of Large-Cap Stocks:
✅ Stability & Reliability: These stocks are less volatile compared to small-caps.
✅ Regular Dividends: Many large-cap companies distribute dividends, making them attractive for long-term investors.
✅ Strong Market Presence: Recognized brands with global influence.
⚠️ Risks Involved:
❌ Lower Growth Rate: Since these companies are already established, their expansion rate is slower.
❌ Expensive Valuations: High demand often leads to premium pricing.
🔹 Example Large-Cap Stocks:
- Reliance Industries: ₹17,00,000 Cr
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS): ₹14,50,000 Cr
- HDFC Bank: ₹12,00,000 Cr
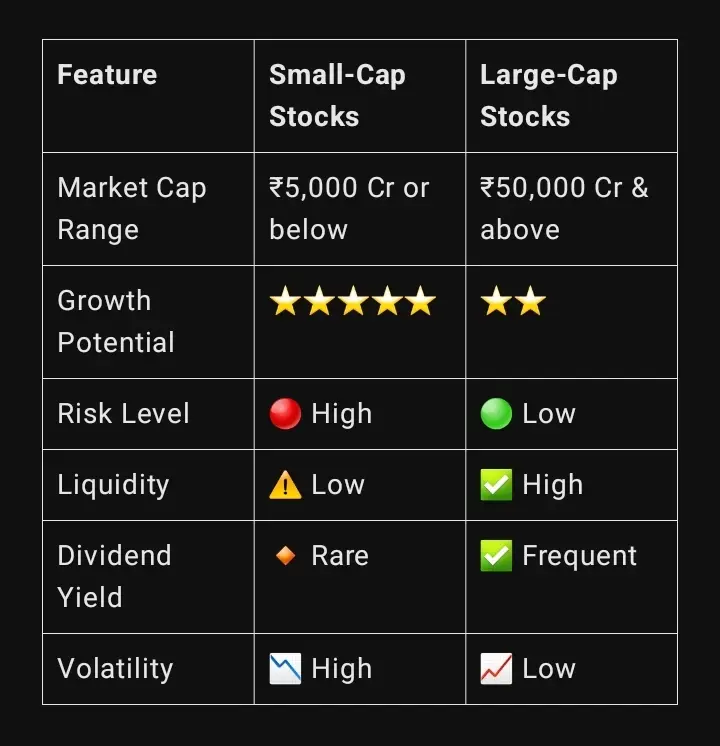
Small-Cap vs. Large-Cap: Key Differences
Which One Should You Choose?
Your investment decision should align with your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals:
🔹 If you seek aggressive growth and can tolerate high volatility, small-cap stocks may be suitable.
🔹 If you prefer stable returns with lower risk, large-cap stocks are a safer choice.
Tip: Diversifying your portfolio with a mix of both small-cap and large-cap stocks can help balance risk and reward.
Final Thoughts
Both small-cap and large-cap stocks have their own advantages and risks. Smart investing requires thorough research, patience, and a well-diversified approach. Whether you go for high-growth small-caps or stable large-caps, always align your choices with your financial goals.
📌 Stay updated on market trends, analyze company fundamentals, and invest wisely!




