Investing in the stock market requires a solid strategy to maximize returns. There are two primary approaches to stock analysis: Fundamental Analysis (FA) and Technical Analysis (TA). Understanding their differences can help you make informed trading decisions.
🔍 Fundamental Analysis (FA)
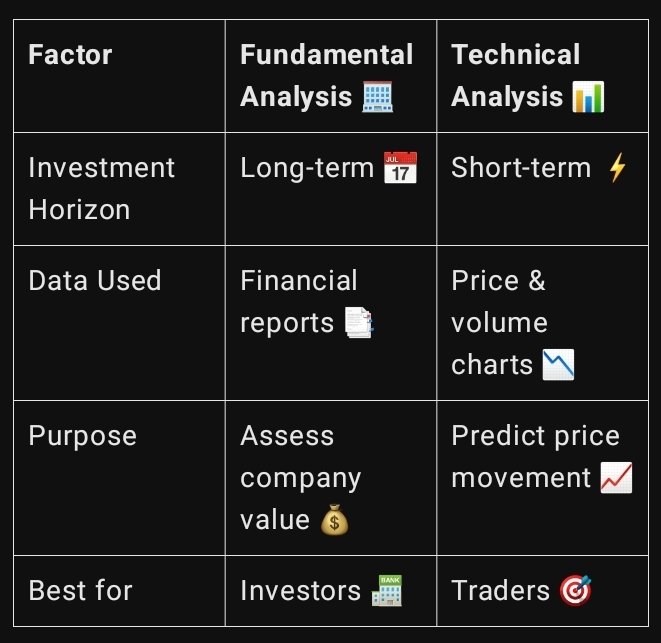
Fundamental analysis evaluates a company’s financial health, market position, and future growth potential. This method is ideal for long-term investors who want to invest in fundamentally strong companies.
Key Factors in Fundamental Analysis:
📌 Financial Statements: Analyze income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements to assess profitability and stability.
📌 Earnings & Revenue Growth: A consistent rise in revenue and net profit indicates a company’s financial strength.
📌 P/E Ratio (Price-to-Earnings): Measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings. A low P/E ratio may indicate an undervalued stock.
📌 P/B Ratio (Price-to-Book): Compares a company’s market value to its book value. A P/B ratio below 1 suggests an undervalued stock.
📌 Debt-to-Equity Ratio (D/E): A lower ratio indicates financial stability, while a higher ratio suggests higher risk.
📌 ROE & ROA (Return on Equity & Assets): Measures how efficiently a company generates profit from shareholders’ equity and total assets.
📌 Competitive Advantage: Companies with a strong brand, patents, or market leadership tend to outperform competitors in the long run.
📌 Industry & Market Trends: Analyzing sector performance and economic trends helps gauge future growth potential.
⏳ Best for: Long-term investors & value investors.
📈 Technical Analysis (TA)
Technical analysis focuses on price movements and trading volume to predict future stock prices. Traders use charts, patterns, and indicators to find buying and selling opportunities.
Key Tools in Technical Analysis:
📊 Price Charts: Candlestick charts, line charts, and bar charts help visualize price movements.
📊 Support & Resistance: Identifying key levels where stocks tend to bounce or break out helps traders make informed decisions.
📊 Moving Averages (MA):
- SMA (Simple Moving Average): Averages stock prices over a specific period.
- EMA (Exponential Moving Average): Gives more weight to recent prices for quicker trend identification.
📊 RSI (Relative Strength Index): Measures stock momentum. A reading above 70 indicates overbought conditions, while below 30 suggests oversold conditions.
📊 MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Helps spot trend reversals and momentum shifts.
📊 Volume Analysis: Higher trading volume during an uptrend confirms a strong bullish move.
📊 Chart Patterns: Patterns like Head & Shoulders, Double Bottom, Cup & Handle, and Triangle formations indicate potential breakout or breakdown points.
⚡ Best for: Short-term traders, swing traders & day traders.
🏆 Fundamental vs. Technical Analysis: Which One is Better?
🔹 A hybrid approach combining both FA and TA can be highly effective. Investors can use FA to find quality stocks and TA to determine the best entry and exit points.
✅ Final Thoughts
Both fundamental and technical analysis have their merits. Long-term investors benefit from fundamental analysis, while short-term traders rely on technical analysis. Choosing the right method depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
🚀 Whether you are a fundamental investor or a technical trader, mastering stock analysis will enhance your decision-making and boost your trading success!
🔔 Stay informed & trade wisely!




